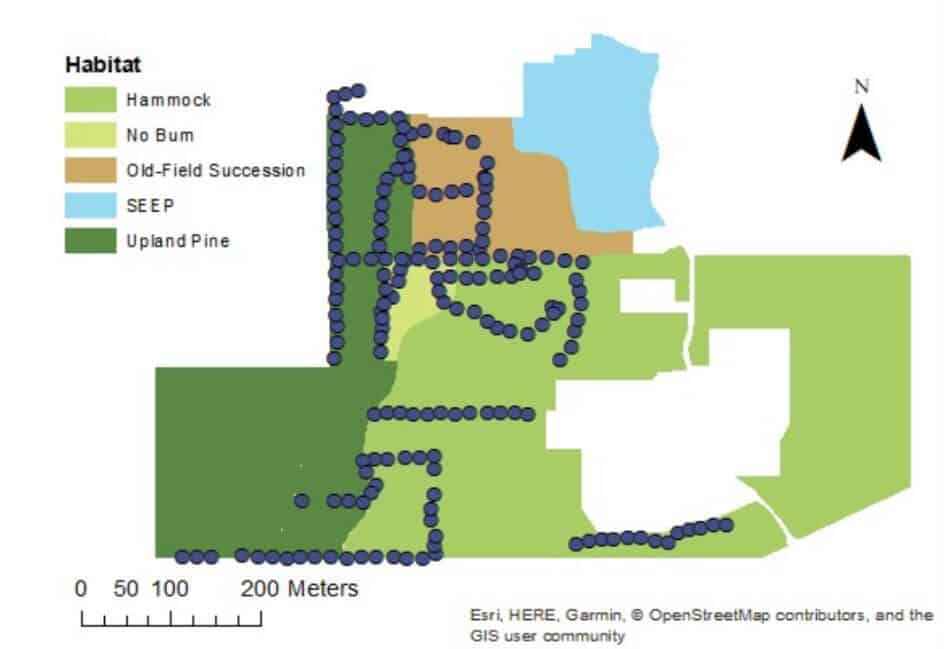
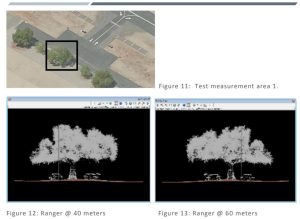
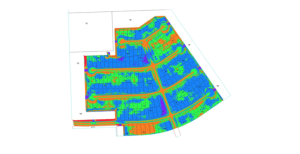
Remote sensing techniques have many applications for natural resource management and conservation, such as habitat analysis, measuring forest carbon stocks, protected area delineation, landscape modeling, and human impact surveys (e.g., logging, mining). Currently, among the remote sensing methodologies, light detection, and ranging (lidar) is the most accurate tool for quantifying forest structure characteristics.
These measures are accurate in a wide range of forested ecosystems and even have applications in urban settings. Unlike photogrammetric systems which use passive sensors requiring sunlight to illuminate the area of interest, lidar sensors actively emit laser pulses to create three-dimensional point clouds. When point cloud density is high, lidar can be used for measuring tree height, identifying tree species, estimating crown canopy profile, estimating biomass, and generating carbon projections at various spatial scales. Lidar sensors can be satellite or aircraft-borne, deployed above and below the canopy with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), or ground-based.