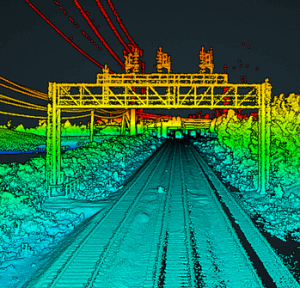
In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems introduces the fundamentals of LiDAR technology. You’ll learn about the purpose of LiDAR, its applications, how it works, and its components. LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing tool used to measure 3D features quickly and accurately. It’s widely used in vegetation mapping, utility management, roadway construction, mining, and bathymetric mapping.
The video explains how LiDAR emits laser pulses to measure distances, with the system recording the time it takes for the light to return. This data, combined with positioning and orientation information from GPS and IMU sensors, creates a detailed 3D point cloud. Multiple returns from a single pulse allow LiDAR to capture data through vegetation and other obstacles.
This video also highlights practical uses of LiDAR data, such as estimating tree height, measuring power line sag, and detecting changes in topography.
Interested in learning more about how LiDAR works? Read our more in depth article on LiDAR fundamentals.