Videos

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems introduces the Ranger-LR, his personal favorite and the most adaptable LiDAR system available. Known as the “universal soldier” of LiDAR mapping systems, the Ranger LR can be used on UAVs, helicopters, and mobile vehicles, offering unmatched versatility for both aerial and ground applications.
The Ranger-LR features the Riegl VUX-1LR22 LiDAR sensor with five-millimeter precision at a 150-meter range and a powerful 1550-nanometer laser that penetrates dense vegetation. It has a maximum range of 1000 meters on 20% reflectance targets and can achieve up to 15 target returns per laser pulse for enhanced vegetation mapping. It collects over 190 points per square meter at 400 feet above ground level from a UAV and over 30 points per square meter at 550 feet from a helicopter.
Ideal for corridor mapping, topography, urban surveying, archaeology, agriculture, and rapid response applications, the Ranger-LR is designed for those seeking a highly adaptable and precise LiDAR system.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems explains the meaning behind the term “survey grade LiDAR” and explores different grades of LiDAR with their benefits and drawbacks. Corey delves into the history and context of survey grade accuracy, highlighting how modern tools achieve precise measurements. He defines survey grade accuracy, typically around 10 centimeters or better, and discusses the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing’s positional accuracy standards.
The video covers various accuracy classes of LiDAR, from one centimeter to over three meters, and explains their applications. It emphasizes the importance of choosing the right LiDAR system for specific needs, whether it’s high accuracy drone-based surveys or large-scale mapping projects. Phoenix LiDAR Systems offers a range of solutions that meet these varying requirements, ensuring precise and reliable results.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems walks you through the five essential steps to process LiDAR data after collection. Starting with raw data, he explains how to transform it into an optimized, colorized, and classified point cloud.
The steps include: post-processing the trajectory to correct flight path errors, generating a point cloud by fusing LiDAR measurements with the optimized trajectory, refining the point cloud’s accuracy with the LiDAR Snap tool, colorizing the point cloud with RGB values from the system’s camera, and classifying the point cloud to extract and segment features like ground, vegetation, and buildings.
This video also demonstrates how these steps are performed using Phoenix LiDAR’s SpatialExplorer software, highlighting the improvements at each stage. By following these steps, you can create accurate 3D models and data derivatives such as digital elevation models, contour maps, and vegetation analysis.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems explains the technology required to produce high-accuracy drone-based LiDAR data. Corey delves into the hardware components necessary for LiDAR acquisition, including the GNSS antenna and receiver for positioning, the IMU for orientation, the LiDAR sensor for measuring angles and distances, a CPU for real-time calculations, and an SSD for data storage.
The video demonstrates how these components work together to generate accurate 3D point clouds and offers tips for optimizing data accuracy, such as using a GNSS reference station and performing boresight alignment calibration. Understanding these technologies and best practices ensures the highest quality drone-based LiDAR data for various applications.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems explains how LiDAR technology impacts five critical industries and enhances everyday life. He explores LiDAR applications in surveying, utility management, roadway construction, mining, and maritime operations.
In surveying, LiDAR is used to map topography for floodplain analysis, property surveys, and land development, offering increased accuracy and safety. Utility management benefits from LiDAR by monitoring vegetation encroachment on power lines and assessing damage to pipelines, railways, and waterways, ensuring timely maintenance and safety. In roadway construction, LiDAR helps with planning, as-built mapping, and maintenance assessments, reducing project time and enhancing road safety.
The mining industry uses LiDAR for accurate volume measurements and safe monitoring of mining operations, while maritime applications rely on bathymetric LiDAR for underwater mapping, ensuring safe boat passage and efficient shipping of goods.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems introduces the fundamentals of LiDAR technology. You’ll learn about the purpose of LiDAR, its applications, how it works, and its components. LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing tool used to measure 3D features quickly and accurately. It’s widely used in vegetation mapping, utility management, roadway construction, mining, and bathymetric mapping.
The video explains how LiDAR emits laser pulses to measure distances, with the system recording the time it takes for the light to return. This data, combined with positioning and orientation information from GPS and IMU sensors, creates a detailed 3D point cloud. Multiple returns from a single pulse allow LiDAR to capture data through vegetation and other obstacles.
This video also highlights practical uses of LiDAR data, such as estimating tree height, measuring power line sag, and detecting changes in topography.
Interested in learning more about how LiDAR works? Read our more in depth article on LiDAR fundamentals.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems guides viewers on choosing the right DJI M300 mountable LiDAR solution. He compares the Phoenix Recon XT and the MiniRanger 3, both of which are high-performance, survey-grade systems adaptable for UAV and mobile mapping applications. He also highlights the intrinsic differences between a higher-powered single laser system and a lower-powered multi-laser system to help users understand their specific use cases.
The video showcases real-world applications of these systems. It includes a detailed look at a project site where Scott McGowan from Kestrel Aerial uses the MiniRanger 3 Lite and the Recon XT. The MiniRanger 3 Lite, known for its precision and adaptability, excels in high-density point collection and meets USGS quality level 0 specifications. The Recon XT, valued for its performance in dense vegetation and its wide vertical field of view, is ideal for environments with heavy foliage.
Throughout the video, viewers see practical demonstrations of each system’s capabilities, including data visualization and analysis. The video concludes with a recap, emphasizing the importance of selecting the appropriate LiDAR system for specific project requirements, whether for land development, utility infrastructure, or vegetation mapping.

In this video, Kory Kellum from Phoenix LiDAR Systems discusses selecting the right tool for high altitude LiDAR mapping, focusing on the Ranger series. Phoenix LiDAR Systems offers the Ranger XL, Ultra, and Ranger LR, which excel in long-range capability, precision, accuracy, and point density. These systems are the lightest and highest performing on the market, capable of a 1.5 megahertz measurement rate, over a 750-meter range on 20% reflectance targets, and can produce up to 15 returns per pulse, meeting USGS quality level zero specifications.
Kory details the similarities of the Ranger systems, including their weight, performance, and compatibility with UAVs and crewed aircraft, before exploring their differences and specific use cases. The Ranger XL is ideal for high altitude mapping with a wide field of view and fast data acquisition, making it perfect for high point density corridor mapping such as power line, railway track, and pipeline inspection. It has the longest range in the Ranger lineup, suitable for high altitude projects with fixed-wing or rotorcraft.
The Ranger Ultra combines weight, range, accuracy, and pulse rate with a unique forward and rear-looking field of view to minimize laser shadowing. It features a three-faceted mirror for improved vertical surface mapping and is ideal for UAV-based high point density corridor mapping projects requiring precision and accuracy.
The Ranger LR is the most adaptable, designed for demanding mapping applications with a 360-degree field of view, making it compatible with mobile, UAV, and helicopter-based mapping. It can penetrate dense vegetation and offers unparalleled versatility.
Kory emphasizes that the Ranger series provides turnkey solutions for various mapping needs, whether for wide area, corridor, or adaptable mapping applications. He encourages viewers to like, subscribe, and contact the sales team to find the right tool for their specific needs.
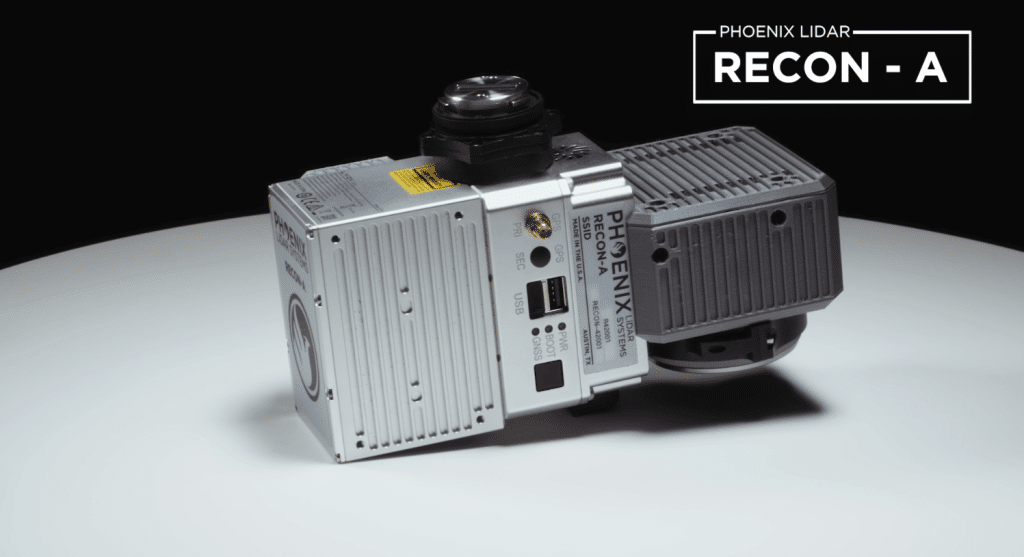
The Phoenix RECON-A is the premier solution for reconnaissance mapping missions, including vegetation encroachment on powerlines. This all-in-one payload offers user-friendly operation and efficient data collection at a competitive price point. The RECON-A enhances point cloud density with its multi-pattern laser, effectively capturing even the lowest reflective points. Additionally, the integrated 24 MP high-resolution camera shares the same field of view as the LiDAR sensor, ensuring optimal RGB colorization of the point cloud.
Explore available Phoenix LiDAR Systems to see how the Recon-A compares with other LiDAR systems.