Product

Join the Phoenix LiDAR Systems webinar on advanced imaging systems, held on April 21, 2021. Hosted by Conrad Conterno, Head of Post-Processing, and Justin Wyatt, VP of Sales at Phoenix LiDAR Systems, along with Nick Nelio, Inspection Sales Manager for Phase One, this session dives into how Phoenix LiDAR’s data collection tools integrate with Phase One’s cutting-edge imaging systems to enhance remote sensing capabilities.
Conrad Conterno opens with an overview of Phoenix LiDAR’s custom mapping solutions, emphasizing LiDAR sensor integration for superior data acquisition and analysis. He introduces various advanced camera options, including the lightweight custom A6K Light for UAV-based mapping, dual oblique cameras for enhanced colorization, multispectral solutions for detailed vegetation analysis, thermal mapping cameras for environmental monitoring, and hyperspectral sensors for precise spectral analysis.
Nick Nelio then showcases Phase One’s high-resolution, medium-format cameras, focusing on the 4-band solution that combines RGB and near-infrared imagery, ideal for crop analysis and environmental monitoring. He also presents the Phase One P3 payload for inspection applications and the IX Mach 5 controller designed for efficient geospatial missions.
Throughout the webinar, the benefits of direct geo-referencing and the seamless integration of multiple sensors into single payloads are highlighted. The hosts address audience questions on the accuracy of dual-camera systems, post-processing challenges, and the applications of hyperspectral imaging.
The session concludes with Justin Wyatt and Nick Nelio emphasizing their collaborative approach to delivering tailored solutions and inviting viewers to contact them for personalized consultations.

Join Phoenix LiDAR Systems in their March 2021 webinar as they unveil their latest software releases, Spatial Explorer 6 and 6 Pro. Hosted by Terry Owens from the sales team and Conrad Conterno, head of post-processing, this informative session provides an in-depth overview of Phoenix LiDAR’s innovative multi-platform solutions and industry-leading advancements.
Learn about the comprehensive features of Spatial Explorer 6 and 6 Pro, from basic sensor control and data export to advanced calibration and post-processing tools. Discover how the new A-to-Z workflow integrates NavLab for seamless trajectory processing, and explore enhanced features like automated bore sighting, LiDARSnap, and CameraSnap for optimized data accuracy.
The webinar also includes a detailed Q&A session, addressing compatibility, geoid applications, and software comparisons, with insights from CTO Ben Adler. Don’t miss this opportunity to see how Spatial Explorer 6 Pro can streamline your LiDAR data processing and deliver superior results.
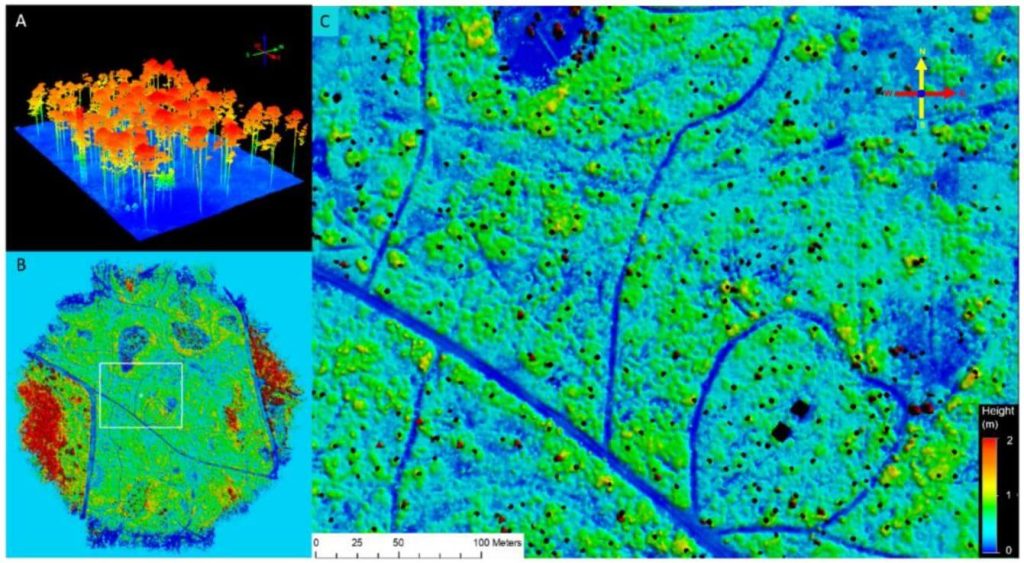
This whitepaper explores the application of high-density UAV-borne LiDAR technology for monitoring understory dynamics in the pine savannas of the southeastern United States, particularly in the context of prescribed fire management. Traditionally, understory characteristics such as height and biomass have been monitored through field sampling, but this study contrasts these conventional methods with advanced remote sensing techniques.
Utilizing the GatorEye UAV system, LiDAR data provided spatially explicit estimates of understory height and biomass before and after a prescribed fire. The results showed significant correlations between LiDAR-derived measurements and traditional field data, demonstrating the accuracy and efficiency of LiDAR technology.
Notably, LiDAR’s comprehensive spatial coverage revealed a smaller biomass reduction after the burn compared to in-situ measurements, highlighting the importance of capturing spatial variability. The findings underscore the potential of LiDAR as a powerful tool for land managers, offering enhanced spatial and temporal resolution in tracking understory biomass and its response to fire, ultimately supporting more effective ecosystem management practices.
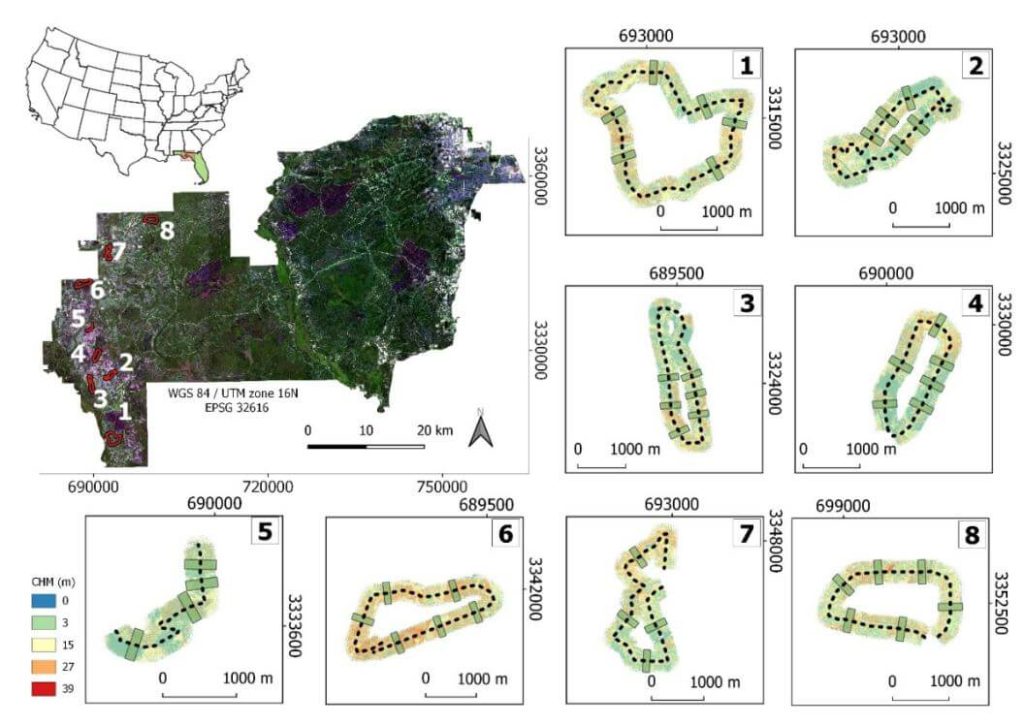
This whitepaper examines the efficiency and accuracy of UAV-borne LiDAR, specifically the GatorEye system, for high-resolution forest data acquisition, comparing it to traditional aircraft-borne LiDAR in the Apalachicola National Forest, USA. The study assesses the effectiveness of single-pass flight plans for generating digital terrain models (DTMs) and canopy height models (CHMs).
Results indicate that DTMs derived from UAV LiDAR showed less than 1 meter difference compared to aircraft-derived DTMs within a 145° field of view (FOV). CHMs provided reliable treetop detection, though tree height underestimations occurred at distances over 175 meters from the flight line. Crown segmentation was effective within a 60° FOV, but shadowing effects hindered its accuracy beyond this range.
The study identifies optimal quality thresholds for various LiDAR products, supporting the development of efficient, cost-effective UAV flight plans for forest monitoring. These findings highlight the potential of UAV-borne LiDAR for detailed, multi-temporal forest structure assessment, offering valuable insights for forest management and conservation strategies.
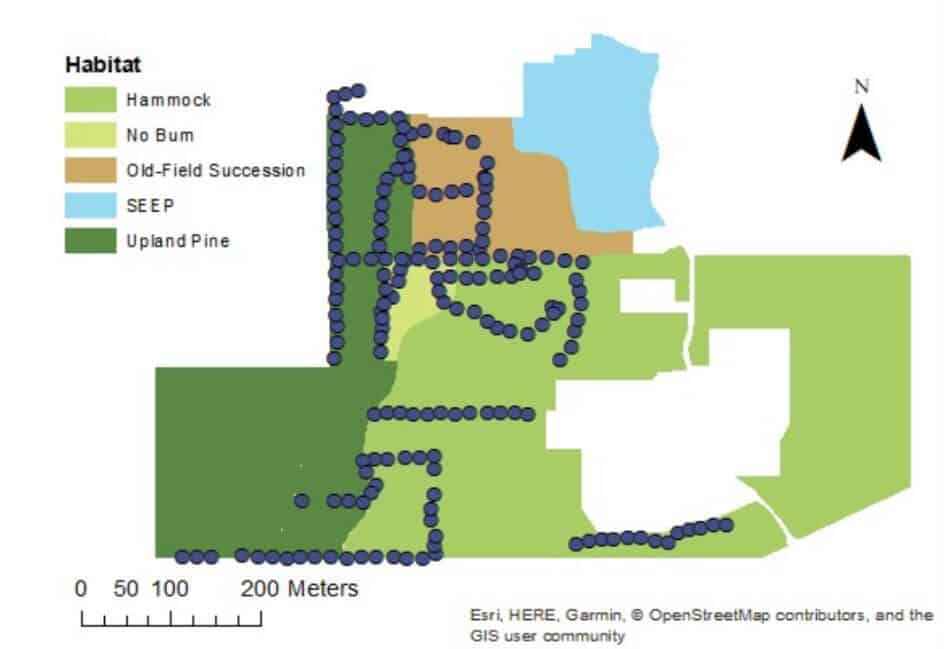
This whitepaper explores the effectiveness of UAV-borne LiDAR technology for detecting small trails (less than 2.5 meters wide) in mixed forest canopy ecosystems. Accurate trail mapping is crucial for forest management, monitoring, and conservation, yet current sensor technology for sub-canopy detection is still evolving.
The study compares trail detectability using high-definition surface models from UAV LiDAR data and high-resolution satellite imagery from Google Earth. Through participatory mapping, respondents with limited geospatial experience identified trails on both map types. Results showed higher detection rates on the LiDAR-derived map compared to the satellite imagery. In satellite maps, trail detectability was positively correlated with wider trails and lower canopy cover, whereas LiDAR maps showed increased detectability with wider trails regardless of canopy cover.
This mixed-method approach, combining UAV-mounted LiDAR, satellite imagery, and participatory mapping, enhances the rapid detection of small trails under varying conditions, offering valuable insights for improving forest management and conservation efforts.
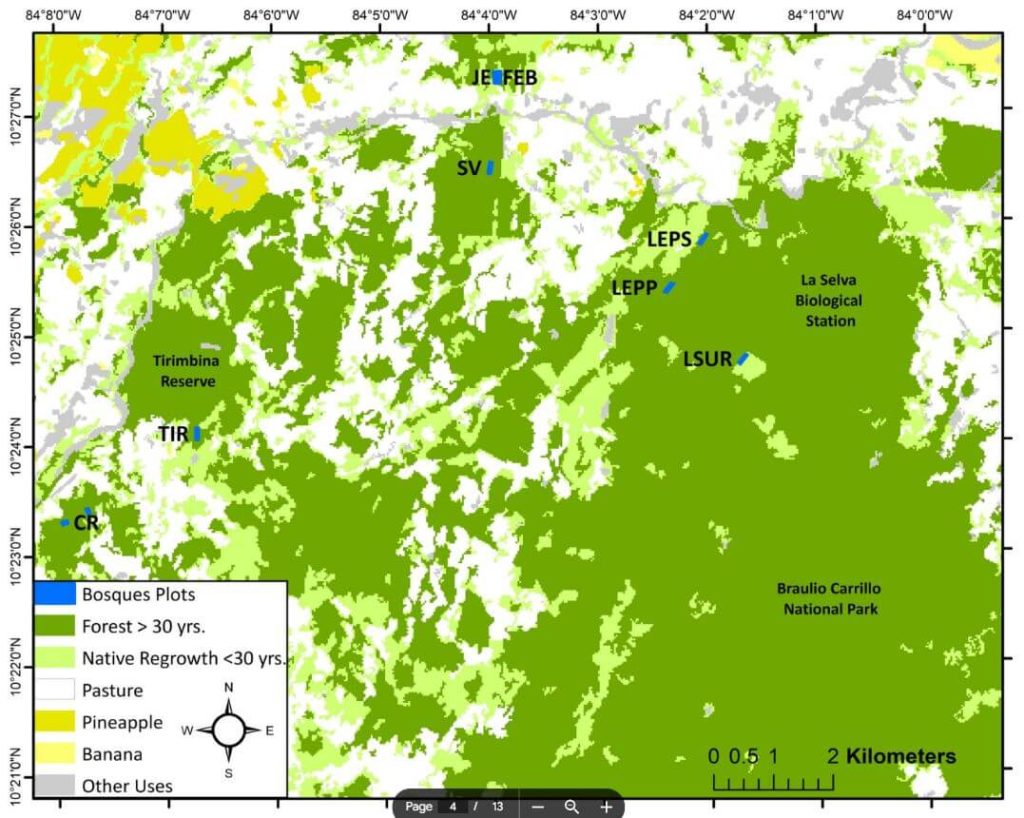
This whitepaper investigates the innovative application of the GatorEye drone-borne LiDAR system for monitoring tropical forest succession through detailed canopy structural attributes. These attributes include canopy height, spatial heterogeneity, gap fraction, leaf area density (LAD) vertical distribution, canopy Shannon index, leaf area index (LAI), and understory LAI.
Focusing on nine tropical forest stands in the Caribbean lowlands of northeastern Costa Rica, the study evaluates the relationship between these variables and aboveground biomass (AGB) stocks and species diversity. The analysis reveals that while canopy height and AGB do not show a clear pattern with forest age, gap fraction and spatial heterogeneity increase, and understory LAI decreases as forests age.
Notably, canopy height is strongly correlated with AGB. The study demonstrates that drone-LiDAR systems significantly enhance the characterization of heterogeneous mosaics created by successional forest patches in human-managed landscapes. This technology offers a valuable tool for improving forest recovery assessments and developing mechanistic carbon sequestration models, crucial for tracking progress within the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration.
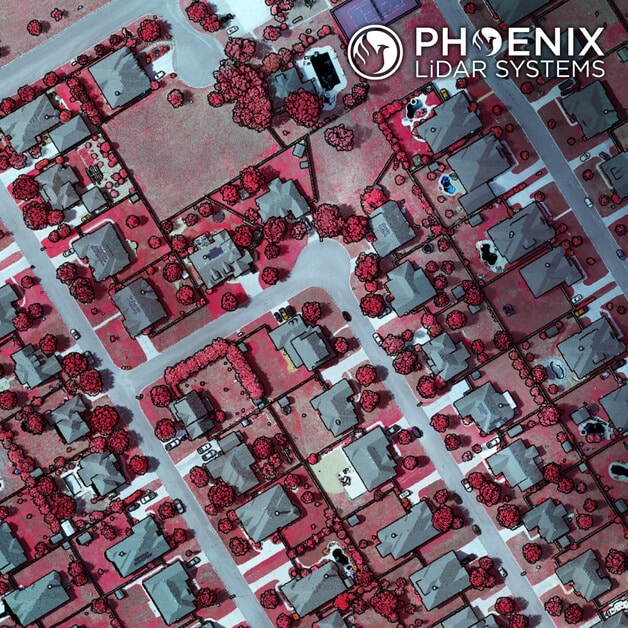

A few weeks ago we posted a video of a completed Ranger-XL ready for shipment. Here’s a peek at a recent dataset collected by that same Ranger-XL coupled with the 100MP Phase One 4-band Solution. This urban corridor was easily captured with a single pass, creating a stunning dataset with high Imagery and LiDAR resolution. Data specs: 80 Points Per Square Meter Average for LiDAR and 3cm GSD for imagery.
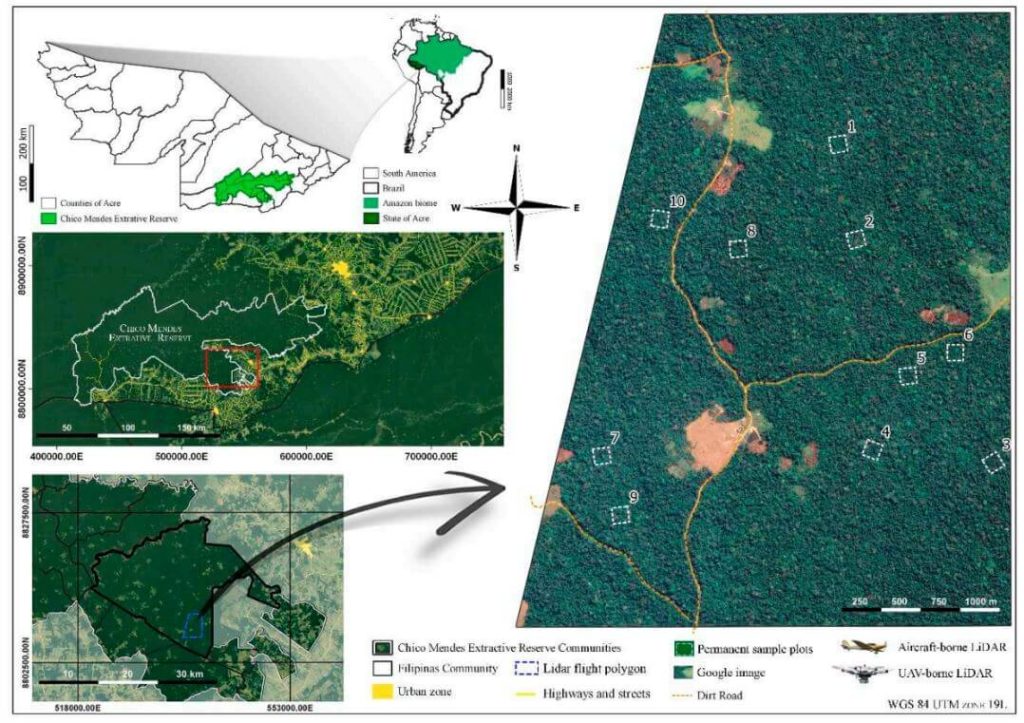
This whitepaper explores the challenges of obtaining high-quality forest structure information in tropical forests, particularly those in difficult-to-access areas. Traditional field-based approaches are often costly and time-consuming, prompting the use of LiDAR technology for efficient and comprehensive structural parameter estimates.
The study compares aboveground biomass (AGB) estimations and products from aircraft-borne LiDAR data collected in 2015 with data from the UAV-borne GatorEye Unmanned Flying Laboratory in 2017 across ten forest inventory plots in the Chico Mendes Extractive Reserve in Acre, southwestern Brazilian Amazon.
Findings indicate that both platforms produce comparable LiDAR products, with the GatorEye system demonstrating higher point density due to its lower and slower flight and increased returns per second. Despite these differences, ground point density remained similar between the systems.
Both sensors yielded analogous results for digital elevation models and estimated AGB. This study validates the effectiveness of UAV-borne LiDAR sensors in accurately quantifying AGB in dense tropical forests and highlights the potential for detailed analyses of crown structure and leaf area density distribution using dense point clouds from UAV systems.
The high dimensionality of data generated by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV)-Lidar makes it difficult to use classical statistical techniques to design accurate predictive models from these data for conducting forest inventories. Machine learning techniques have the potential to solve this problem of modeling forest attributes from remotely sensed data. This work tests four different machine learning approaches – namely Support Vector Regression, Random Forest, Artificial Neural Networks, and Extreme Gradient Boosting – on high-density GatorEye UAV-Lidar point clouds for indirect estimation of individual tree dendrometric metrics (field-derived) such as diameter at breast height, total height, and timber volume.